Machined Parts
We professionally customize machined parts according to your needs and provide the best processing solutions for each part manufactured.
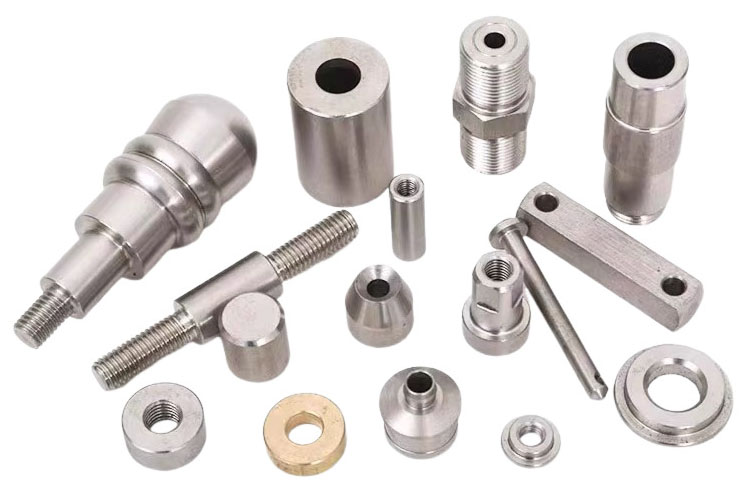
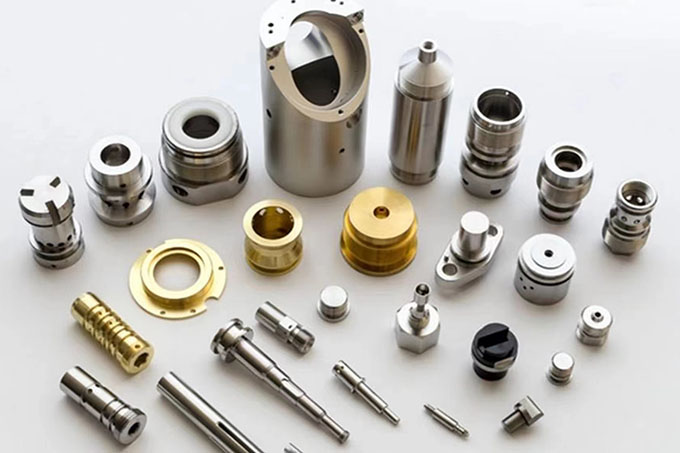


What are machined parts
Mechanical processing refers to the process of accurately removing excess material from the blank through traditional mechanical processing according to the shape and size requirements of the drawing, so that the blank can meet the shape and position tolerances required by the drawing. Modern mechanical processing is divided into two categories: manual processing and CNC processing. Manual processing refers to the operator operating lathes, milling machines, grinders and other mechanical equipment to perform precise processing on the workpiece, which is suitable for single-piece and small-batch parts production; while CNC processing is the operator setting the program language for the CNC equipment. The CNC controls the axis of the CNC machine tool to automatically process as required by identifying and interpreting the program language, which is suitable for large-scale, complex-shaped parts processing. The specific processes of mechanical processing mainly include turning, milling, grinding, clamping, drilling, boring, planing, punching, sawing, as well as electroplating, heat treatment, wire cutting, forging and other methods.
Machining technology
Turning
Turning is to fix the workpiece on a rotating workholding device, and then use a tool to gradually remove the material on the workpiece to obtain the desired shape and size. This processing method is suitable for manufacturing cylindrical parts such as shafts and sleeves. The turning method and tool selection affect the shape and surface roughness of the final product.
Milling
Milling is a process of cutting materials on the workpiece surface by rotating the tool. By controlling the movement of the tool, parts with complex shapes such as planes, concave and convex surfaces, and gears can be manufactured. Milling includes plane milling, end milling, gear milling, contour milling, etc. Each method is suitable for different processing needs.
Drilling
Drilling is the process of cutting material from a workpiece with a rotating drill bit to form a hole of the desired diameter and depth. It is widely used in manufacturing, construction and maintenance. Drilling is often divided into different types, such as conventional drilling, center drilling, deep hole drilling, and multi-axis drilling.
Grinding
Grinding is the process of gradually cutting or removing material from the surface of a workpiece using a grinding tool to obtain the desired shape, size and surface quality. Grinding is usually used to process parts with high precision and high surface quality requirements, such as molds, precision mechanical parts, tools, etc.
Boring
Boring is a process used to machine circular holes inside a workpiece. A rotating tool is used to cut into an existing hole to achieve precise size and flatness. Unlike drilling, which forms a hole by removing material from the surface of the workpiece, boring is done by inserting a tool into the workpiece to cut a hole.
Planing
Planing is the process of removing material from the workpiece surface using a planer to obtain the desired flat surface, precise size and surface quality. Planing is usually used to machine the flat surface of larger workpieces, such as bases, bed frames, etc. It can provide a flat surface for the workpiece, making it suitable for use with other workpieces.
Broaching
Slotting uses slotting tools to gradually deepen the cutting to create complex internal contours. It is often used to process complex shapes such as contours, grooves, and holes of workpieces. Slotting can usually achieve higher processing accuracy and surface quality, and is suitable for parts that require high precision and good surface quality. It is generally divided into plane slotting, contour slotting, groove slotting, hole slotting and other types.
EDM
Electrospark machining uses arc discharge to cut and process conductive materials to obtain high-precision, complex-shaped parts such as molds and tools. It is often used in the manufacture of molds, plastic injection molds, aviation engine parts, medical devices and other fields.
General steps in mechanical parts design
Clarify the functions and performance requirements of components, and understand the working environment and usage conditions of the designed mechanical system.
Generate multiple design schemes through research, analysis and creativity, evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of various schemes, and select the most appropriate concept design scheme.
Based on the conceptual design, preliminary design refinement is carried out, including considerations of geometry, material selection, processing technology, etc. The design of the 3D model is completed using CAD software.
Use CAE software to simulate and analyze to verify the performance and feasibility of components, including structural mechanics, thermals, fluid mechanics and other aspects.
Select appropriate materials based on design requirements and performance requirements, considering the material’s mechanical properties, chemical properties, and machinability.
Determine the processing technology of parts, including manufacturing methods, processing equipment and process flow, and determine the processing accuracy requirements and assembly requirements.
Make samples of parts for trial production, conduct performance tests and reliability verification. Modify and improve the design based on the test results.
Prepare technical documents, including design drawings, process documents, technical specifications, etc. Ensure that the design documents are complete, accurate, and meet the requirements of relevant standards and specifications.
Carry out production according to design drawings and process documents to ensure the manufacturing quality of parts and control of engineering quantity.
Install and debug components to verify the coordinated work of components with the entire mechanical system to ensure its normal operation.
Complete the acceptance of parts and components, evaluate the design process and results, summarize lessons learned, and provide feedback and improvements.
Your most reliable processing partner for custom parts-Chaoyue Machinery
Surpass Machinery is a machining shop. We have the professionals and expertise to operate machine tools and equipment. We provide a wide range of machining services, including full-scale parts planning, procurement, quality and testing. We can meet the needs of small or large batches of parts or prototypes. Contact us now to get a quote.
Advantages of machined parts
Machining reduces the cost of individual parts through efficient production and mass production achieved through automation technology. Advanced CNC machine tools and high-precision technology ensure the accuracy and surface finish of parts. Machining can be customized according to customer needs and prototypes can be produced within the shortest delivery cycle. Machining adapts to the needs of various materials and complex geometric shapes, and achieves good matching and replacement between the same type of parts produced by different manufacturers.
Machining has no minimum order quantity, making it ideal for prototyping, low-volume production, and small companies. It also means that machined parts can be obtained at an affordable cost for low-volume production.
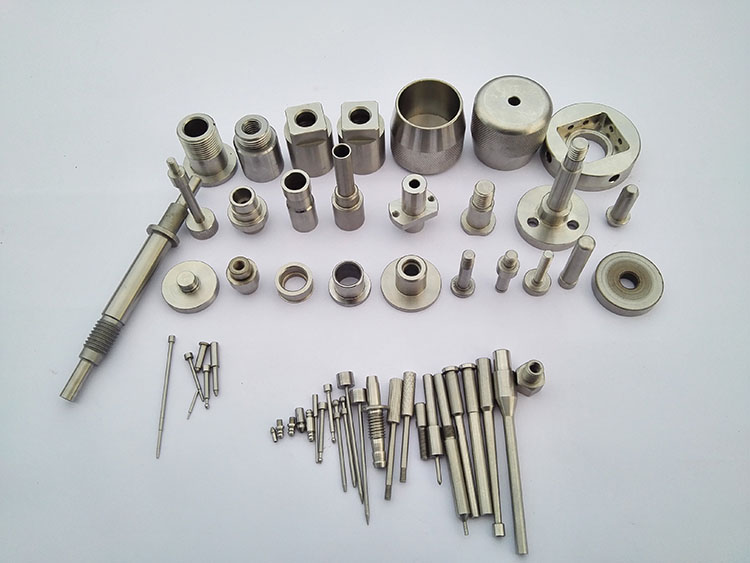

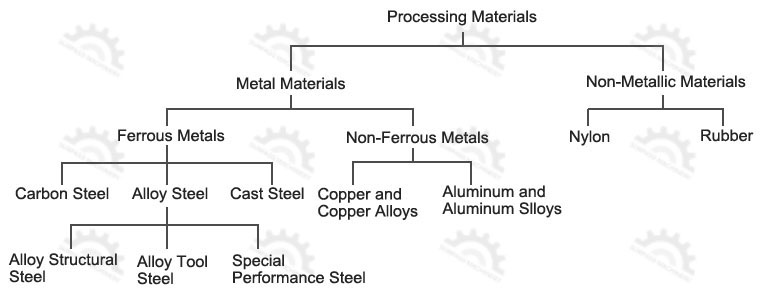
Machining parts materials
In the machining industry, the choice of materials plays a vital role in the quality and performance of products. Different materials have different characteristics and application ranges. The selection of materials for mechanical parts must meet the use requirements, processability and economy. Consider working conditions, load conditions, size quality, importance and special requirements. In terms of technology, structural complexity, blank type and heat treatment performance must be considered. In terms of economy, focus on price, processing costs, material savings and utilization, and material supply. Correctly selecting the right material can improve processing efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure product quality and stability.